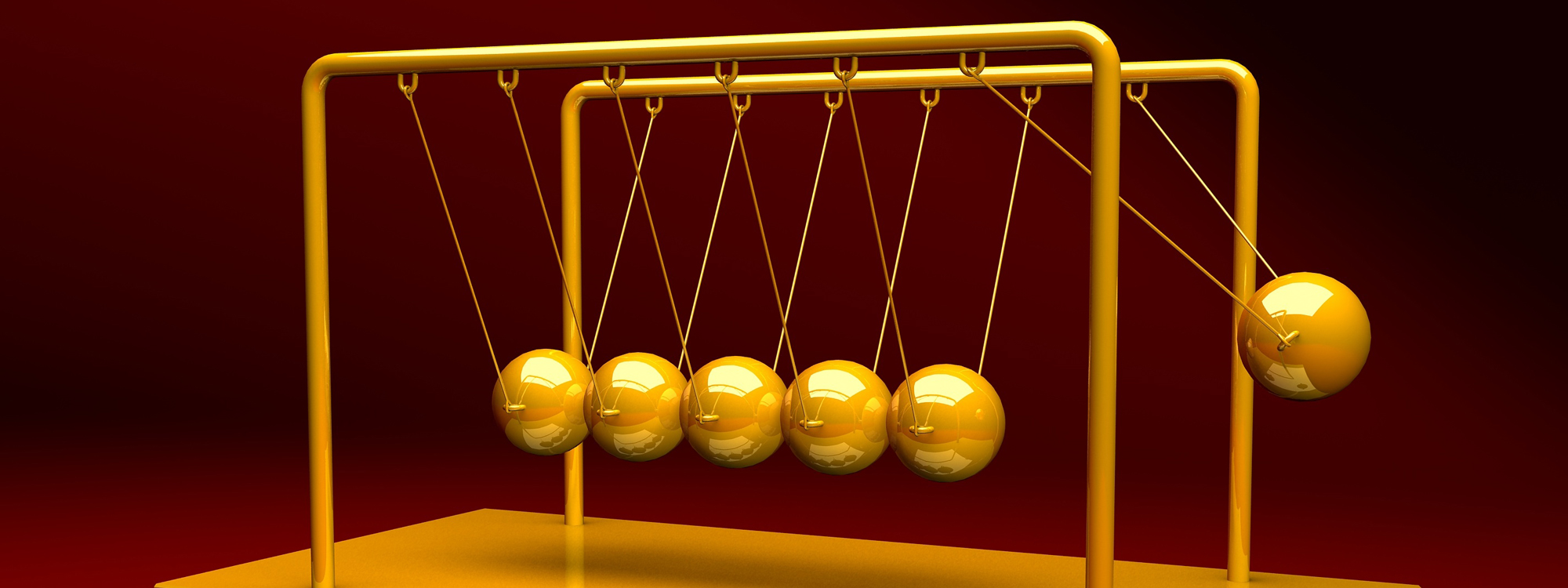
Newton’s cradle is a device that demonstrates conservation of momentum and energy using a series of swinging spheres. When one sphere at the end is lifted and released, it strikes the stationary spheres, transmitting a force through the stationary spheres that pushes the last sphere upward. The last sphere swings back and strikes the still nearly stationary spheres, repeating the effect in the opposite direction. The device is named after 17th-century English scientist Sir Isaac Newton. It is also known as Newton’s Balls or Executive Ball Clicker (since the device makes a click each time the balls collide, which they do repeatedly in a steady rhythm).
A typical Newton’s cradle consists of a series of identically sized metal balls suspended in a metal frame so that they are just touching each other at rest. Each ball is attached to the frame by two wires of equal length angled away from each other. This restricts the pendulums’ movements to the same plane.
Christiaan Huygens used pendulums to study collisions. His work, De Motu Corporum ex Percussione (On the Motion of Bodies by Collision) published posthumously in 1703, contains a version of Newton’s first law and discusses the collision of suspended bodies including two bodies of equal mass with the motion of the moving body being transferred to the one at rest.
Newton’s laws of motion are three physical laws that, together, laid the foundation for classical mechanics. They describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it, and its motion in response to those forces. More precisely, the first law defines the force qualitatively, the second law offers a quantitative measure of the force, and the third asserts that a single isolated force doesn’t exist. These three laws have been expressed in several ways, over nearly three centuries, and can be summarised as follows:
First law
In an inertial frame of reference, an object either remains at rest or continues to move at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by a force.
Second law
In an inertial frame of reference, the vector sum of the forces F on an object is equal to the mass m of that object multiplied by the acceleration a of the object: F = ma. (It is assumed here that the mass m is constant.)
Third law
When one body exerts a force on a second body, the second body simultaneously exerts a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction on the first body.